What is GAAP
GAAP is a collection of accounting standards and common industry usage that have been settled over many years. It is used by organizations to properly organize their financial information into accounting records. To summarize the accounting records into financial statements and reveal certain supporting information.
What does gaap stands for
GAAP Stands for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
One of the reasons for using Generally Accepted Accounting Principles is so that anyone reading the financial statements of multiple companies has a reasonable basis for comparison, since all companies using GAAP have created their financial statements using the same set of rules. GAAP covers a broad selection of topics which includes the following:
List of generally accepted accounting principles
basic gaap principles are listed below
- Assets and Liabilities
- Equity
- Revenue
- Expenses
- Business combinations
- Fair value
- Foreign currency
- Derivatives and hedging
- Leases
- Financial statement presentation
- Non-monetary transactions
- Subsequent events
- Industry-specific accounting, such as airlines, extractive activities, and health care
You may also like to Read:
The industry specific accounting that is allowed or required under GAAP may vary significantly from the more basic standards for certain accounting transactions.
what are the gaap principles
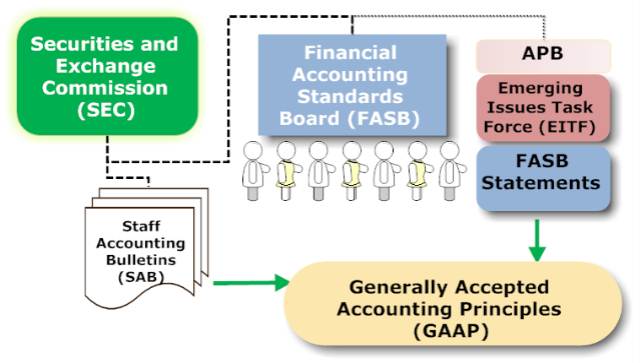
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles is derived from the pronouncements of a series of government-sponsored accounting entities, of which the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the latest. The Securities and Exchange Commission also issues accounting pronouncements through its Accounting Staff Bulletins and other announcements that are applicable only to publicly-held companies and which are considered to be part of GAAP.
why are generally accepted accounting principles (gaap) needed?
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles is used mostly by businesses reporting their financial results in the United States. International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS, is the accounting framework used in most other countries. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles is much more rules-based than IFRS. IFRS focuses more on general principles than GAAP, which makes the IFRS body of work much smaller, cleaner, and easier to understand than GAAP. Since IFRS is still being constructed, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles is considered to be the more comprehensive accounting framework.
There are several working groups that are gradually reducing the differences between the GAAP and IFRS accounting frameworks, so eventually there should be minor differences in the reported results of a business if it switches between the two frameworks. There is a stated intent to eventually merge GAAP into IFRS, but this has not yet occurred. Given recent differences of opinion arising during several joint projects, it is possible that the frameworks will never be merged.
If you want Comprehensive Guide to Understanding GAAP you can visit
