Definition of Markets:
The word ‘market’ invented from Latin word ‘marcatus’ having a verb ‘mercari’ implying ‘merchandise’ ‘ware traffic’ or ‘a place where business is conducted’.
For a layman, the word ‘market’ stands for a place where goods and persons are physically present. For him, ‘market’ is ‘market’ who speaks of ‘fish market’, ‘mutton market’, ‘meat market’, ‘vegetable market’, ‘fruit market’, ‘grain market’. For him, it is a congregation of buyers and sellers to transact a deal.
Though, for us as the teacher of marketing, it means much more. In a bigger sense, it is the whole of any region in which buyers and sellers are brought into contact with one another and by means of which the prices of the goods tend to be equalized easily and quickly.
You may also like to Read:
Classification of Markets
Classification of markets in marketing has been classified in various ways on the basis of different approaches. The important classifications of markets are as follows;
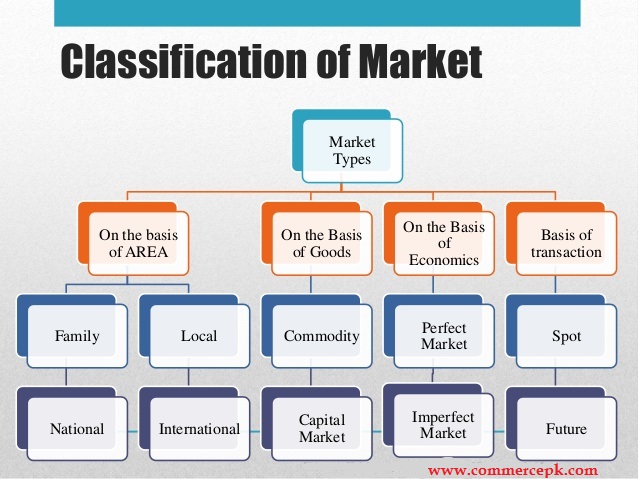
-
Market according to geographical area:
Market on the basis of areas covered is classified into
- Local markets:
Local markets limit to the area mostly dealing in perishable and semi-perishable foods like fish, flowers, vegetables, eggs, milk, and others.
- Regional markets:
The regional market covers a broader area may be a district, a state dealing in durables both consumer and non-durables and industrial products, including agricultural produce.
- National markets:
National markets the area covered are national boundaries dealing in durable and non-durable consumer goods, industrial goods, metals, agricultural produce, forest products,
- International markets:
International market, the movement of goods is extensive all over the world, making it as a single market. It should be noted that due to the latest technologies in transport, storage, and packaging, even the most perishable goods are sold all over the world, not that only durables.
-
Markets on the basis of position of sellers:
Keeping in mind the position of sellers in the market, the markets are classified as under.
- Primary Market:
It is the market where in the farm products are sold by the primary producers to the wholesalers or their agents.
- Secondary market:
It is the market where wholesalers sell goods to the retailers for onward selling it to the consumers.
- Terminal Market:
It is the market where the purchase is finalized by the consumers from the retailers.
- Market on the basis of volume of business Transacted:
On the basis of volume of business transacted, the markets are classified into
- Wholesale markets:
The wholesale market as the name signifies is the market wherein the goods are sold n bulk to the dealers.
- Retail Market:
In a case of the retail market, the goods are sold in small quantity directly to the consumers.
- Markets classification on the basis of nature of transactions:
On the basis of nature of transactions, the market is classified into;
- Spot Market:
The spot market is the cash market. The goods in the spot market are physically transferred from the seller to the buyer.
- Future Market:
In the future market, the purchase or sale of the commodity call for delivery some months in the future. Actual delivery of goods is rarely made.
- On the basis of Time:
Consequently, there can be the short period and long period markets. Short-period markets are for highly perishable goods (such as fruits, vegetables) of all kinds and long-period markets are for durable goods (such as shoes, cloth) of different varieties may be produced or manufactured.
-
Capital Markets:
Capital markets are classified as under
- Money market:
Money markets are those institutions which provide short terms funds to the business.
- Share Market:
These are the organized markets for the purchase and sale of shares of the joint stock companies
- Foreign exchange markets:
These markets trade in foreign currencies.
-
Government Markets and Non-profit :
Companies do sell their products and services to non-profit organizations like temples, churches, universities, charitable institutions and to governmental departments at local, state and central level. The companies that market their products and services have to consider the price aspect because these buyers have limited purchasing power.
Again, lower prices badly affect the features and quality of products and services if an attempt is made to design such an offering.
Hence, these buyers buy through bidding where lowest bid is favored as there is no alternative. They also need the longer period of credit.
If you want to learn more about Types or Classification of Markets you can Visit
