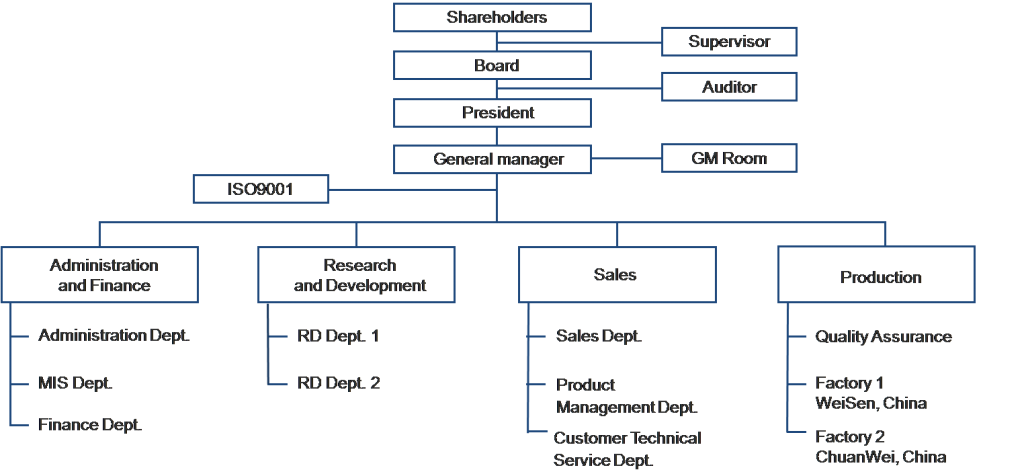
Organizational Structure of a Company
In case of sole tradeship , the business is owned by one person and is operated for one’s own profile. In partnership, all the partners or a few of them take the responsibility of managing the affairs of the firm. In contract to both these forms of organization, the company which is owned by the shareholders is not managed by them.
The shareholders in the annual meeting elect the directors who manage the company according to the policy approved by them. The board of directors thus is the top organ of the company.
The board of director usually forms an executive committee. The chief executive of the committee assisted by head of various departments like;
- production manager
- sales manager
- chief accountant
- personal manager
Manager the company and implement the directors of the board. The organs of the company management are;
You may also like to Read
Basic Organizational Structure of a Company is explained below;
Shareholders:
The shareholders are the owners of a public company. Due to the separation of ownership from control, all the shareholders do not take part in its management. The reasons are;
- They are greater in number and lay scattered in various parts of the country
- They have less at stake compared to the promoters.
- As most of them possess a few shares individually, therefore they are interested in receiving the dividend and are least concerned with the management of the company.
- The majority of the shareholders are ignorant of the operation of the company.
- As a greater number of them have the loose association with the company, they sell the shares in case they receive no dividend or less dividend.
- Due to greater number of absentees of the shareholders in the general meeting, the interested shareholders who are mostly the relatives, friends of the promoters, managers use their voting shareholders who are mostly the relatives , friends of the promoters, managers use their voting right and elect the directors to carry on the internal management of the company by rotation.
Directors of a Company:
In a company form of organization, the ownership is separated from management. The shareholders who are the owner of the company elect directors at the annual general meeting of the company. The elected body called the board of directors is the governing body of the company.
A number of directors: according to company ordinance 1984, a private limited company shall not have less than two directors and a public limited company less than seven directors.
The directors to Act as a Board:
The director acts as a board. they may meet together for the dispatch of business adjourn and otherwise regulate the meeting as they deem fit, the board has the power to delegate certain authority to an individual director or to a committee of directors.
Chairman of the Board;
The director in the meeting elects the chairman who holds office for a period determined by the board. if in a meeting the chairman is not present within 10 minutes after the appointed time of the meeting , the directors can choose any of their members to act as chairman of the meeting.
Quorum:
The quorum for a meeting of directors of a listed public company shall not be less than one-third of their number or four whichever is greater. The board of directors shall meet at least twice in a year.
Power of Directors:
According to section 196 of the company’s ordinance, the business of the company shall be managed by the directors. The directors of a company, by passing a resolution shall exercise the following powers on behalf of the company.
- To issue share
- To issue debentures
- To borrow money otherwise than on debentures
- To invest the funds of the company
- To make loans
- To authorized the directors of the company to enter into any contact with the company for making sale, purchase or supply of goods or rendering services with the company.
- To approve yearly or half yearly or another periodical account as are required to be circulated to the members.
- To approve bonus to employees
- To incur capital expenditure exceeding Rs.35,000 on any single item or to dispose of a fixed asset of the value exceeding Rs.15,000
Chief Executive:
The board of directors of a company is the top organ of management of a company. However, in actual practices, the board appoints one of its directors as the executive chief. This whole time executive is called the chief executive or the managing director of a company. The chief executive has a dual function. He is a director and a chief executive. As the director he shares the responsibilities of the board and as chief executive carries out the management of the company in according with the policies approved by the board.
The companies ordinance 1984 under section 2 (6) has defined chief executive as “an individual who subject to the control and the directions of the directors, is entrusted with the whole or substantially the whole, of the powers of the management of the affairs of the company”. The chief executive is appointed for a period not exceeding three years.
Managing Agent:
The company ordinance 1984 places a bar on the appointment of managing agent’s sole purchase and sole agents etc. According to the Ordinance, no company in Pakistan or outside Pakistan shall appoint any managing agent, by whatever name called, by virtue of an agreement or contract with the company.
Secretary:
The secretary is a salaried officer of the company his appointment as a whole time qualified secretary is made mandatory for a listed as single member company his main job is to carry on the secretarial work.
As secretary is associated with most confidential matters of the company, he should, therefore, be a person who possesses a strong personal sense of responsibility, high moral character, ethical standard and a knowledge of forces that motivates others.
For more explanation about Organization Structure of a company you can visit
